In December 2023, the IMF issued its annual report on the Indian economy under the Article IV Consultation process.
Update
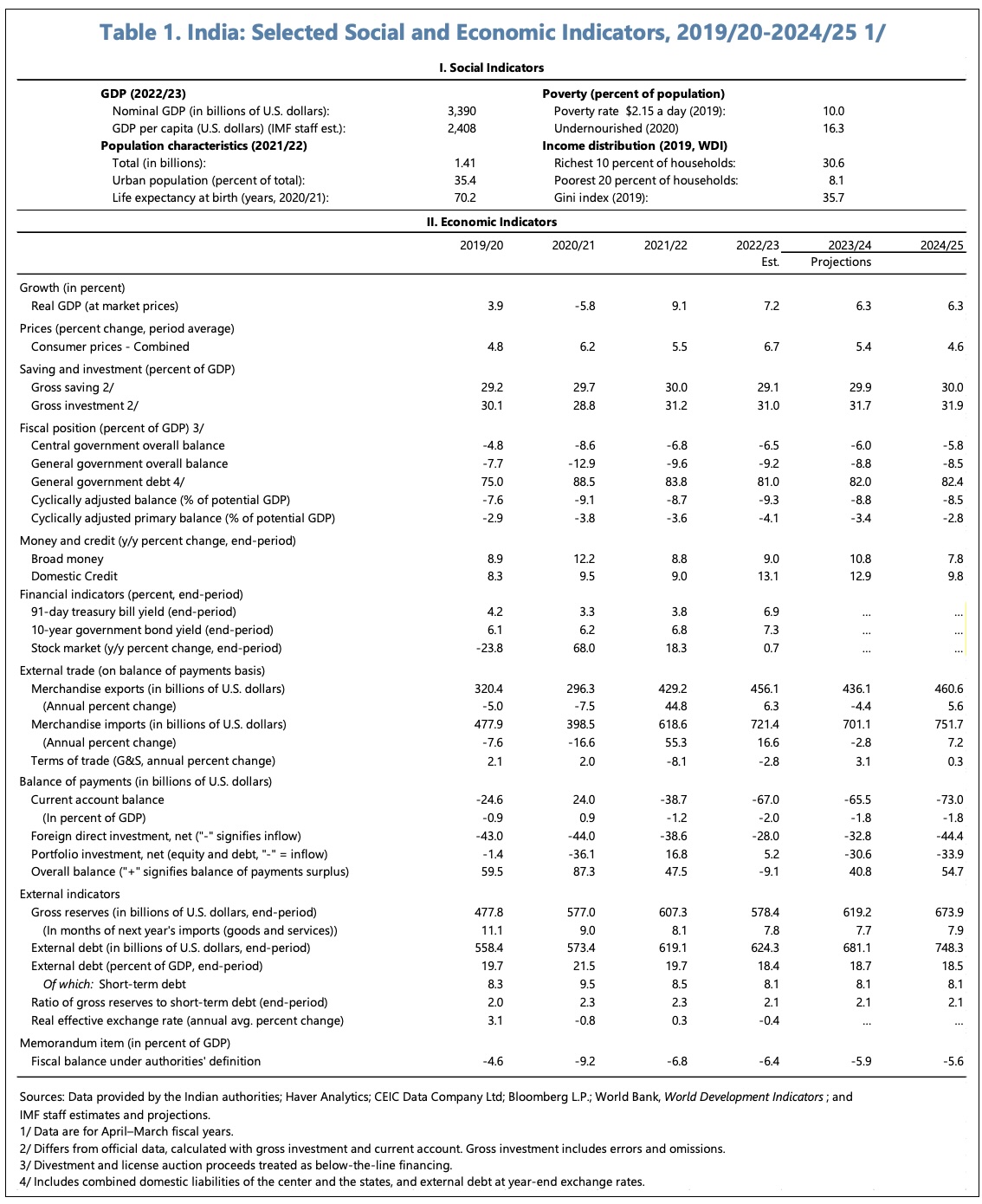
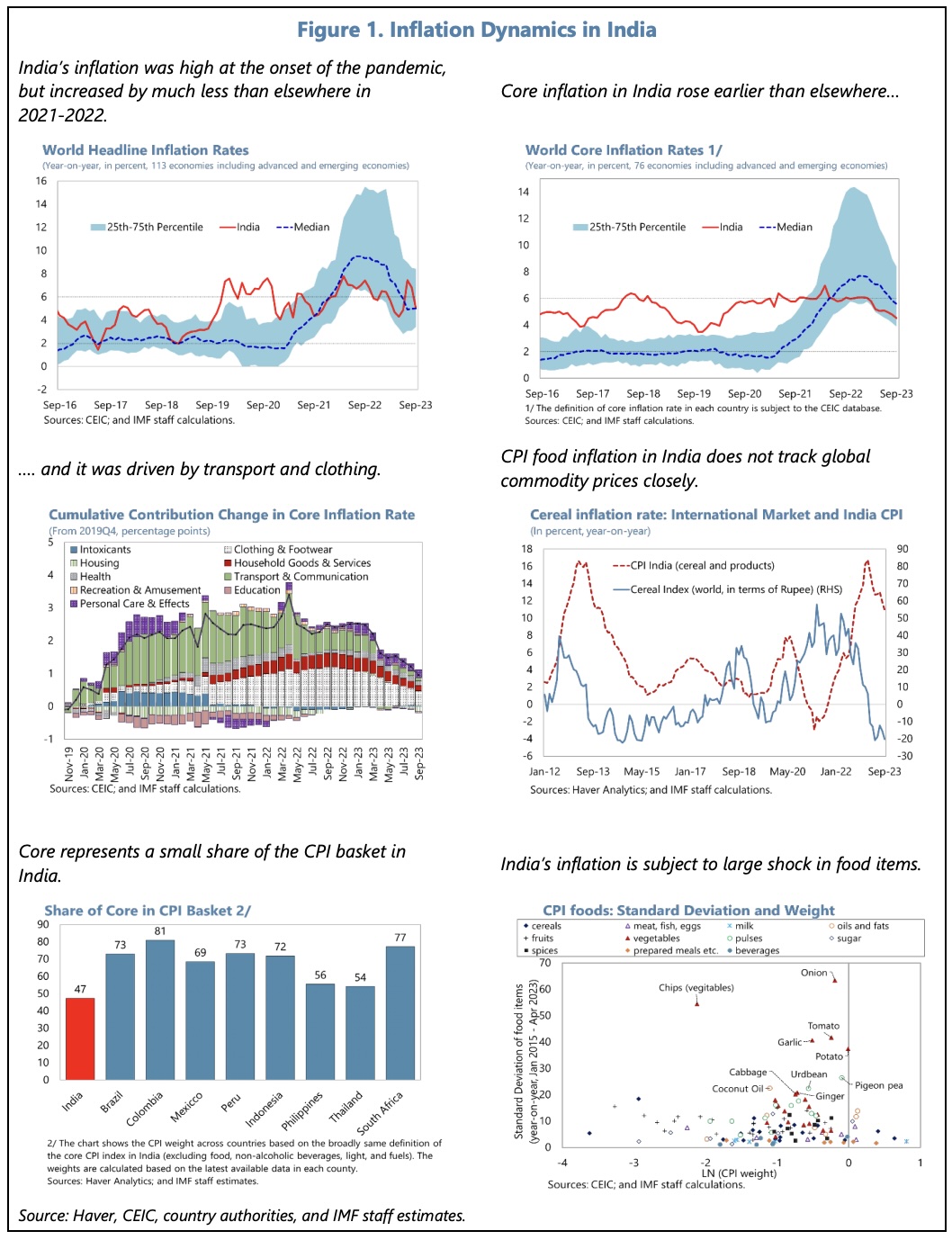
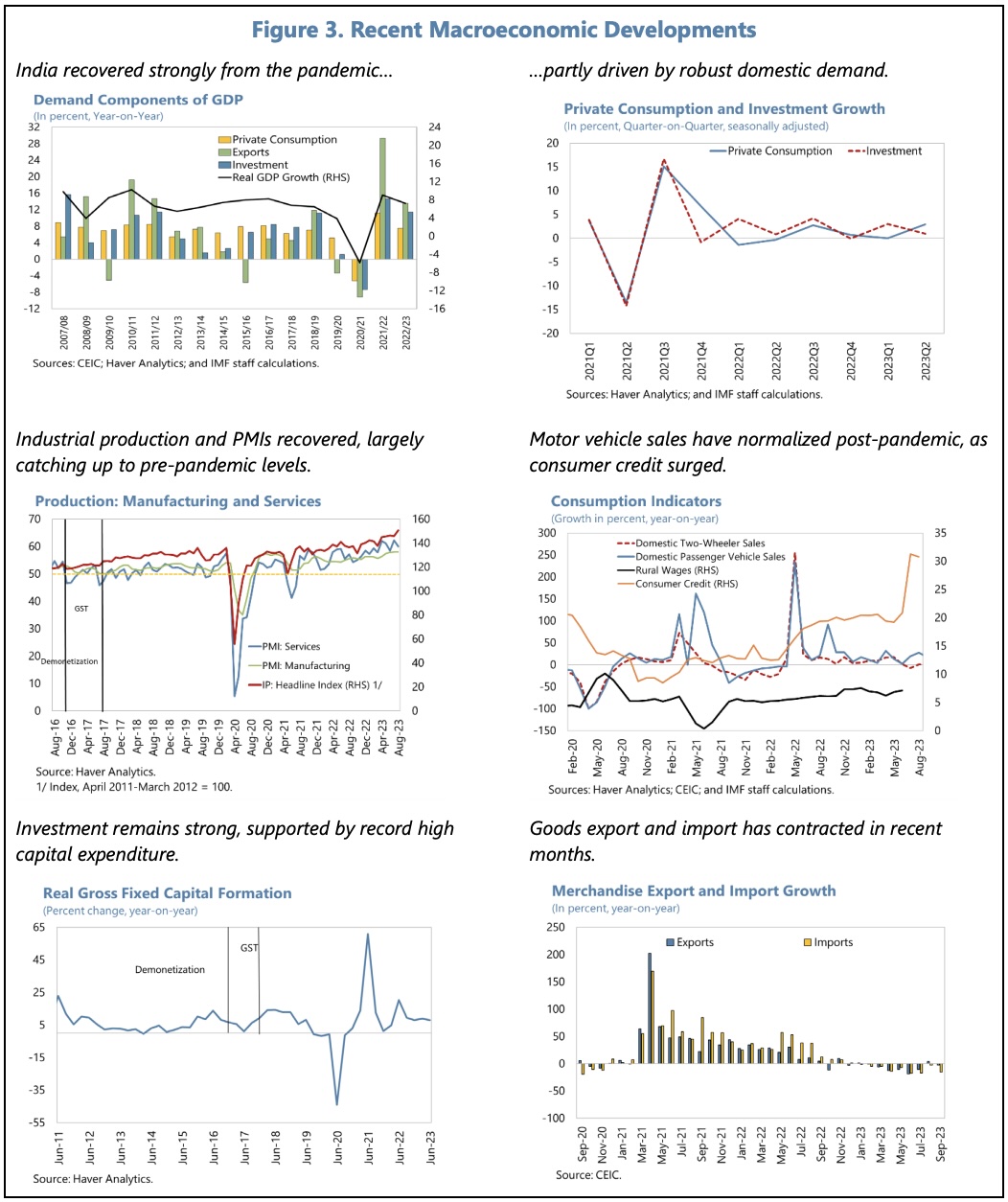
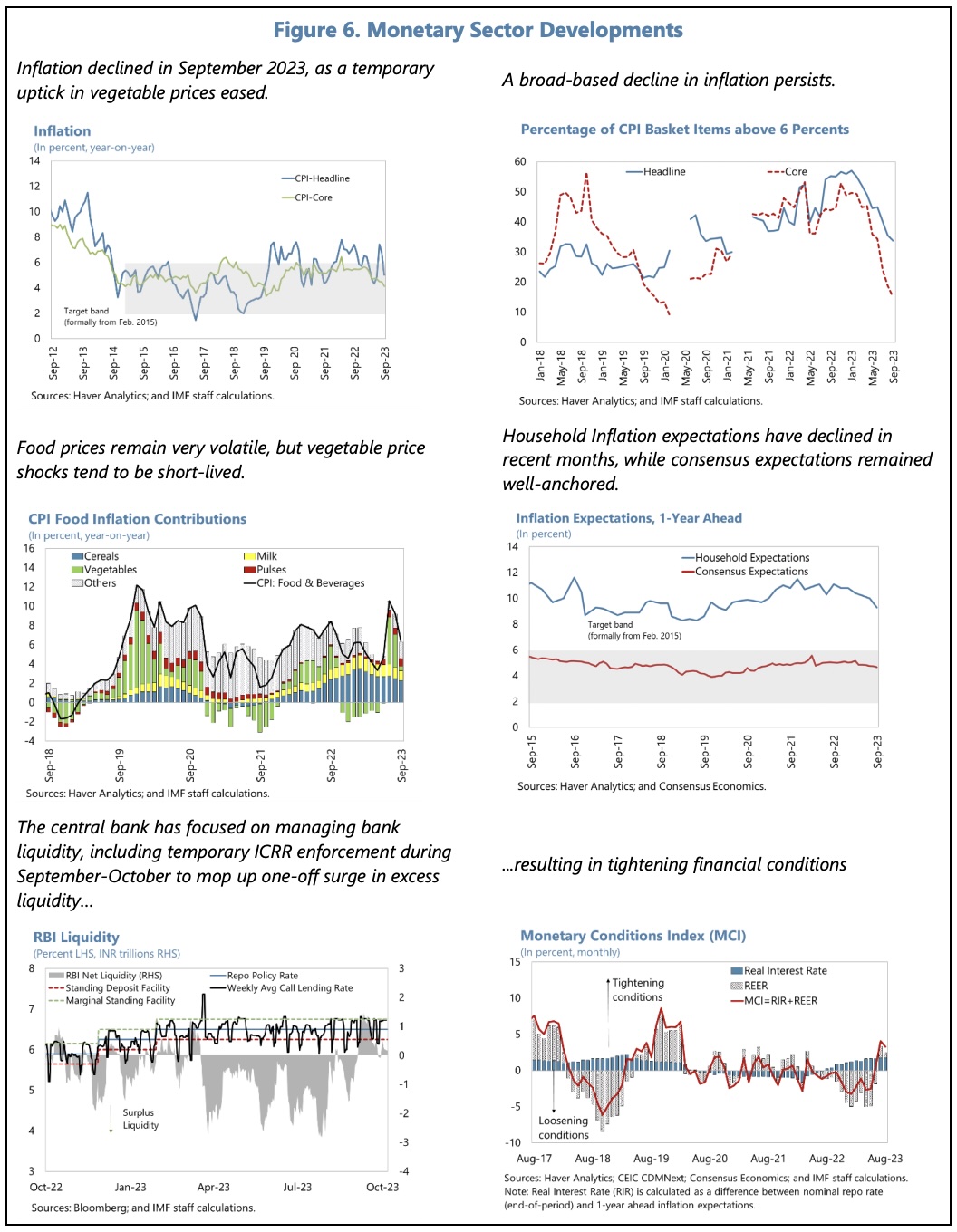
The economy has demonstrated robust growth, and headline inflation, though volatile, has moderated. Employment has passed the pre-pandemic level and, though the informal sector still dominates, formalization has progressed.
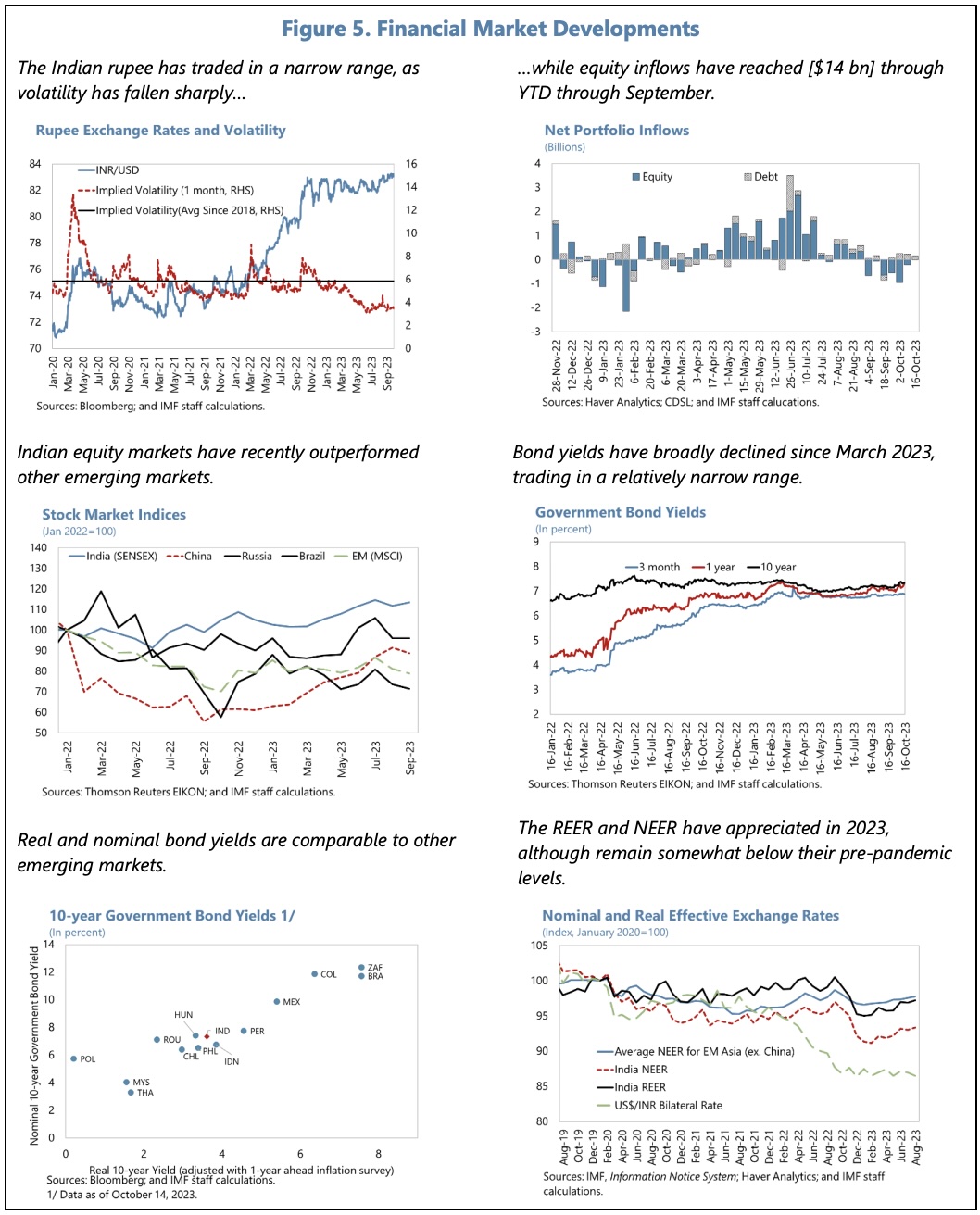
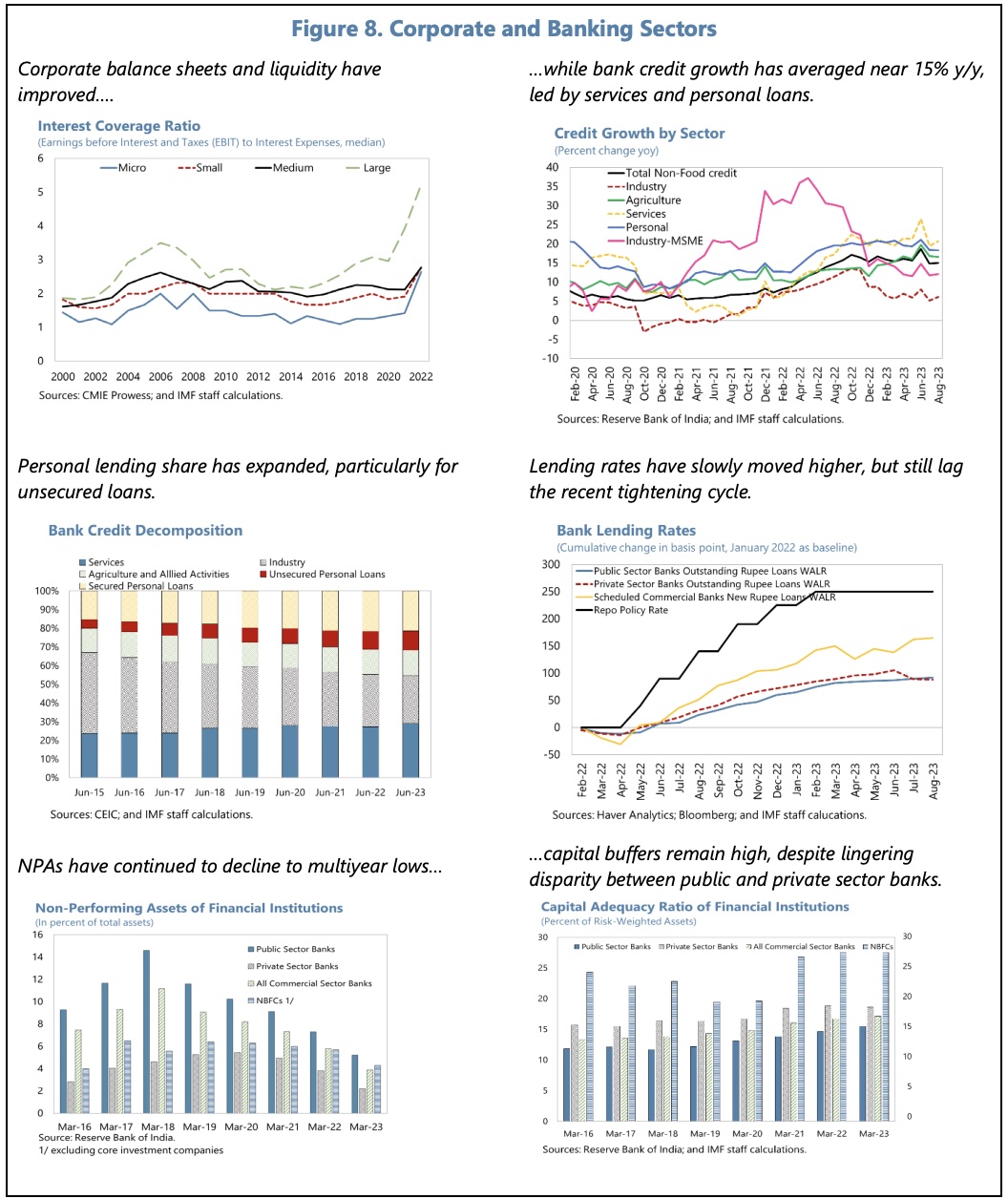
The financial sector has been the strongest in several years and was largely unaffected by global financial stress in early 2023.
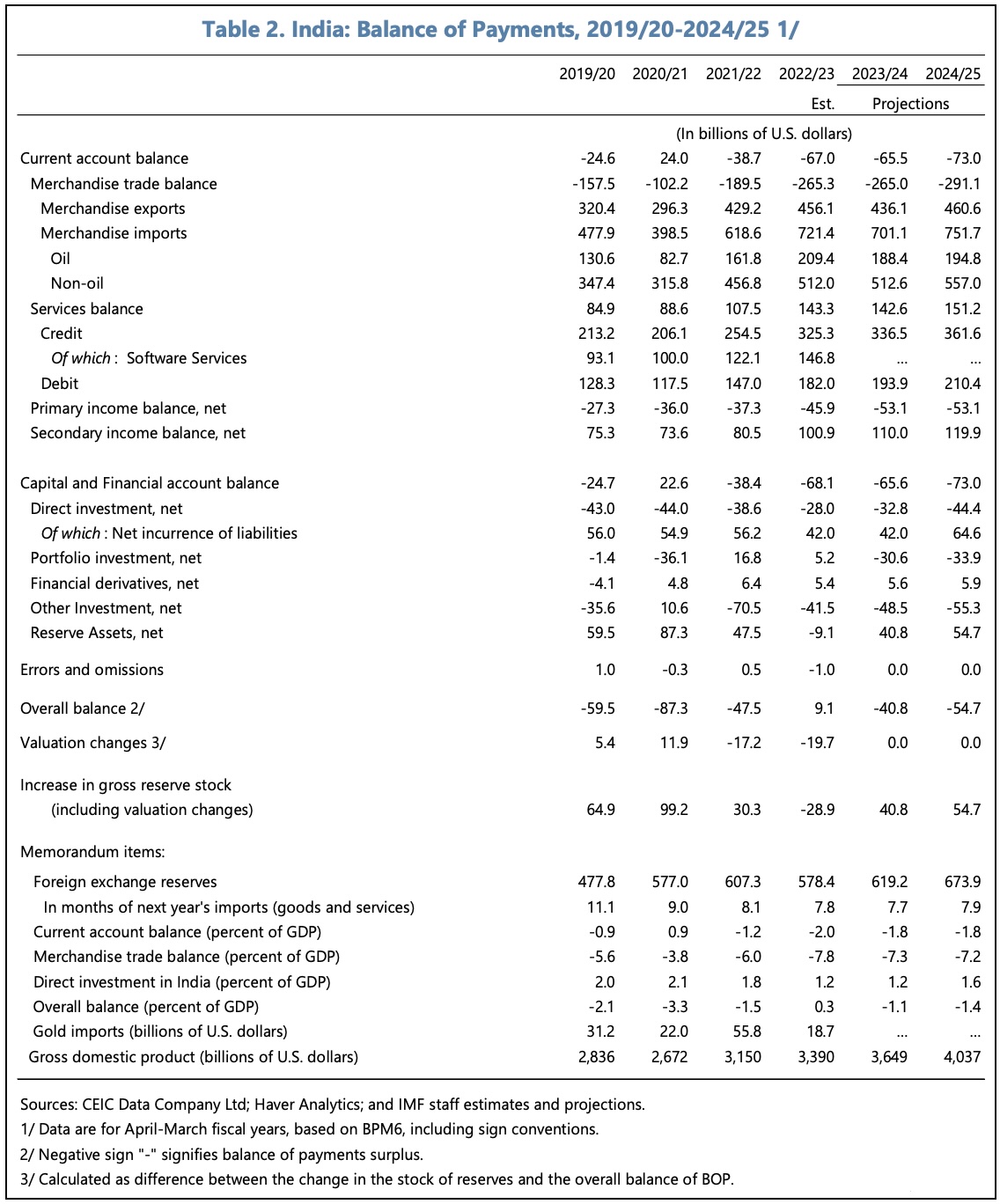
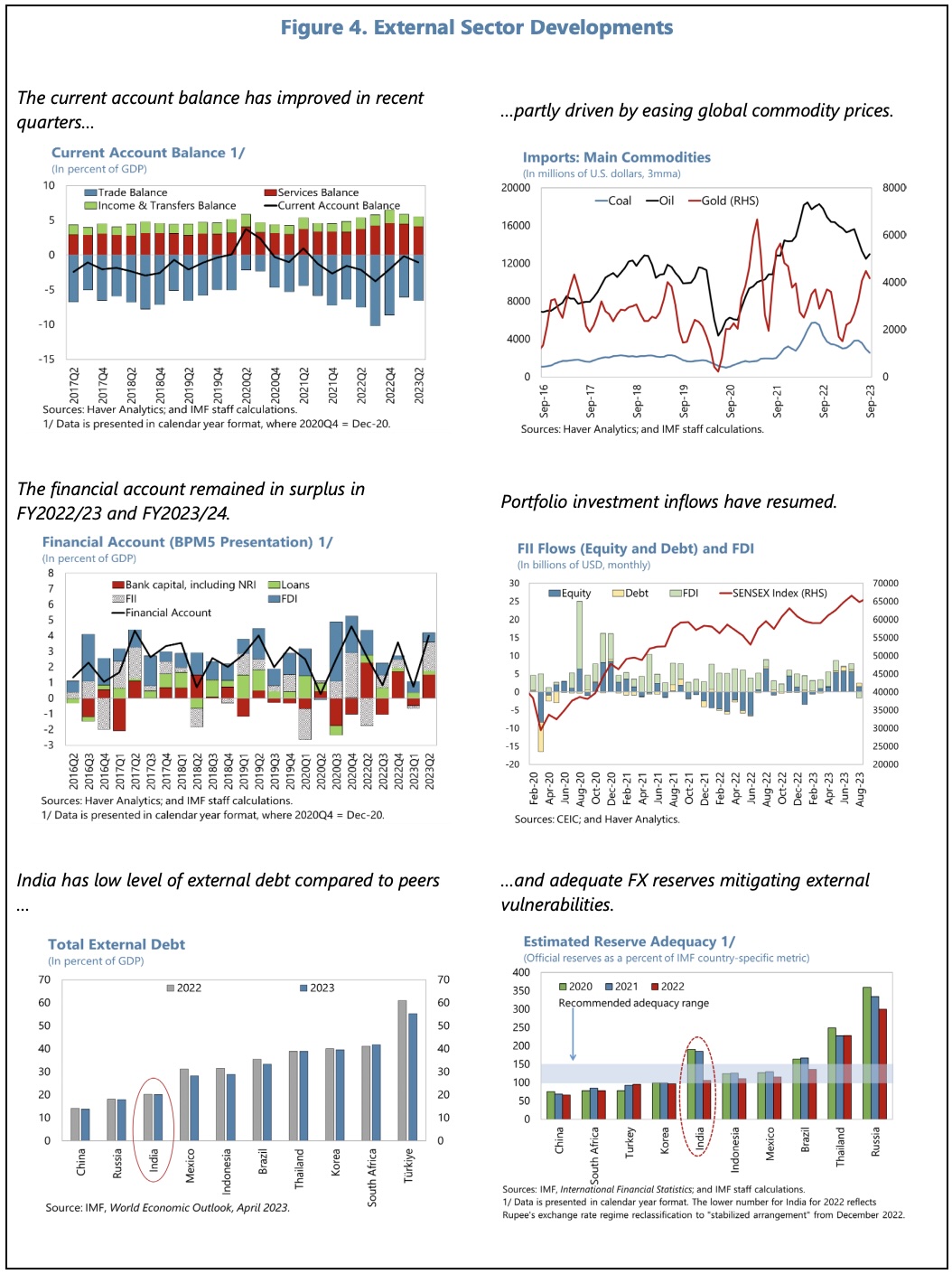
The current account deficit in FY2022/23 widened with the post-pandemic recovery in domestic demand. Transitory external shocks have outweighed the impact of robust services exports and the proactive diversification of oil imports.
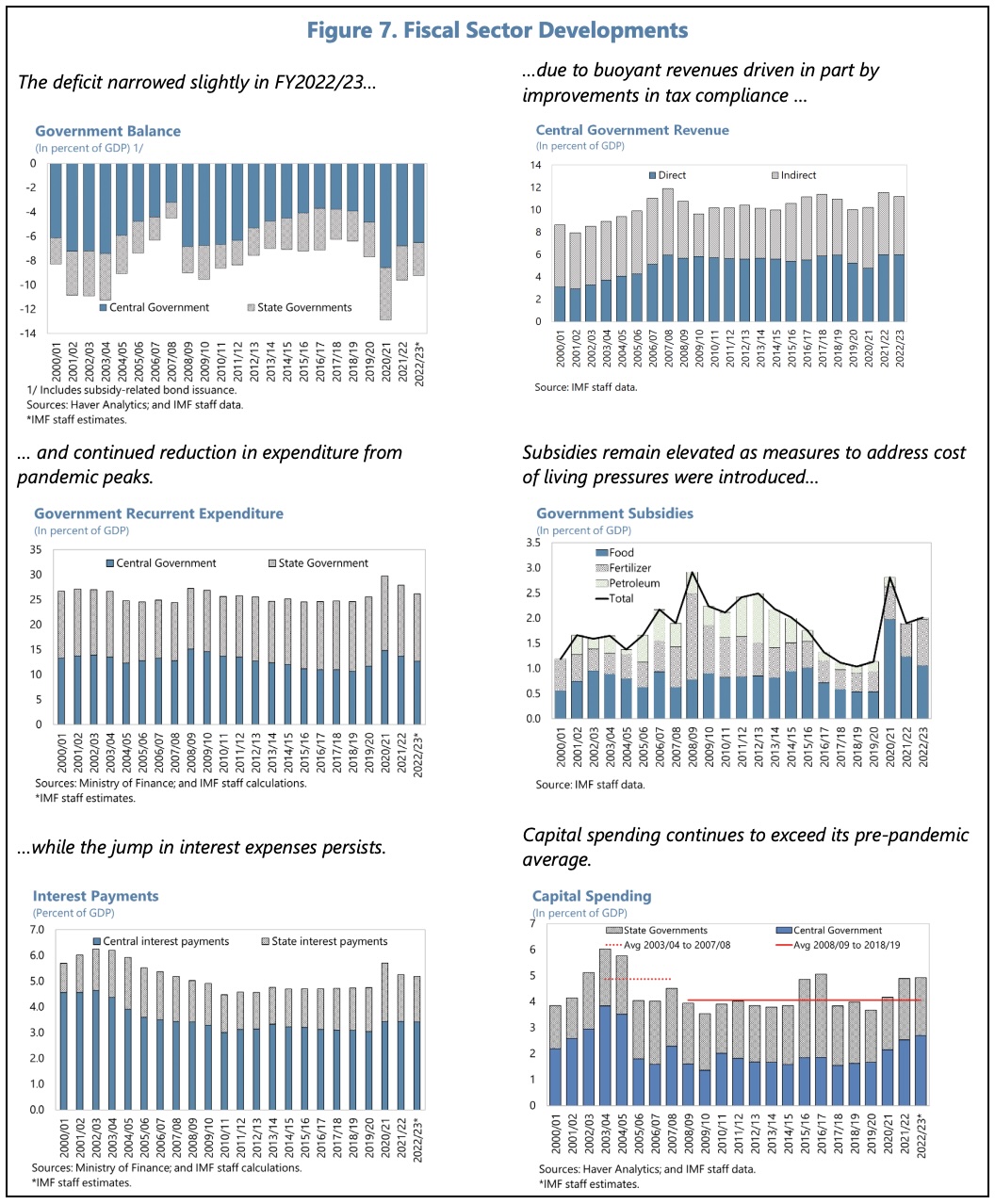
The budget deficit has eased, but public debt remains elevated and fiscal buffers need to be rebuilt.
India’s 2023 G20 presidency has demonstrated the country’s important role in advancing multilateral policy priorities.
Outlook
Growth is expected to remain strong, supported by macroeconomic and financial stability. Real GDP is projected to grow at 6.3% in FY2023/24 and FY2024/25.
Headline inflation is expected gradually to decline to target, although it remains exposed to food price shocks.
The current account deficit is expected to improve to 1.8% GDP in FY2023/24, with resilient services exports and, to a lesser extent, lower oil imports.
Going forward, the country’s foundational digital public infrastructure and a strong government infrastructure program should sustain growth. India has potential for even higher growth, with greater contributions from labour and human capital, if comprehensive reforms are implemented.
Risks to the outlook are balanced. On the downside, external shocks could impact trade and financial channels, whilst weather and commodity prices could impact inflation and the fiscal balance. On the upside, further liberalization of foreign investment could increase India’s role in global value chains, boosting exports. The implementation of labour market reforms could raise employment and growth.
Reform Priorities
The Executive Board has highlighted the following as areas on which to focus reforms:
India’s debt composition mitigates sustainability risks. Nevertheless, ambitious medium-term consolidation efforts are recommended, given elevated public debt levels and contingent liability risks. Specifically, improved revenue mobilization and spending efficiency would allow for continued improvements in digital and physical infrastructure and targeted social support. Putting in place a sound medium-term fiscal framework will promote transparency and accountability, and align policies with India’s development goals.
The directors agree that the current neutral monetary policy stance, anchored on a data dependent approach, should gradually bring inflation back to target. They argue that exchange rate flexibility should remain the first line of defence in absorbing external shocks, and that FX interventions should be limited to addressing disorderly market conditions.
They welcome the stability and resilience of the financial sector, as reflected in sustained growth in bank credit, low levels of non-performing assets, and adequate capital and liquidity buffers. Systemic risks have declined. However, there is scope to strengthen regulatory and supervisory standards. They directors referred specifically to rapid growth in unsecured personal loans and to the need for public banks to continue building capital buffers.
Comprehensive structural reforms focused on job-rich, inclusive and greener growth can help further leverage India’s favourable demographics. Improving labour market functioning and female labour force participation, and making progress on health, education, land, and agricultural reforms remain critical to strong and inclusive growth.
The directors acknowledged India’s efforts to foster new bilateral trade agreements. They broadly stressed that recent restrictive trade policies should be phased out and they supported further liberalizing the FDI regime.
To read the full Article IV report, please use the following link to the IMF’s website:
The following tables and charts summarise some of the IMF’s main thoughts on India’s recent economic performance and outlook.